The True Story of How Laurel Became Yanny
https://ift.tt/2IrsQs4
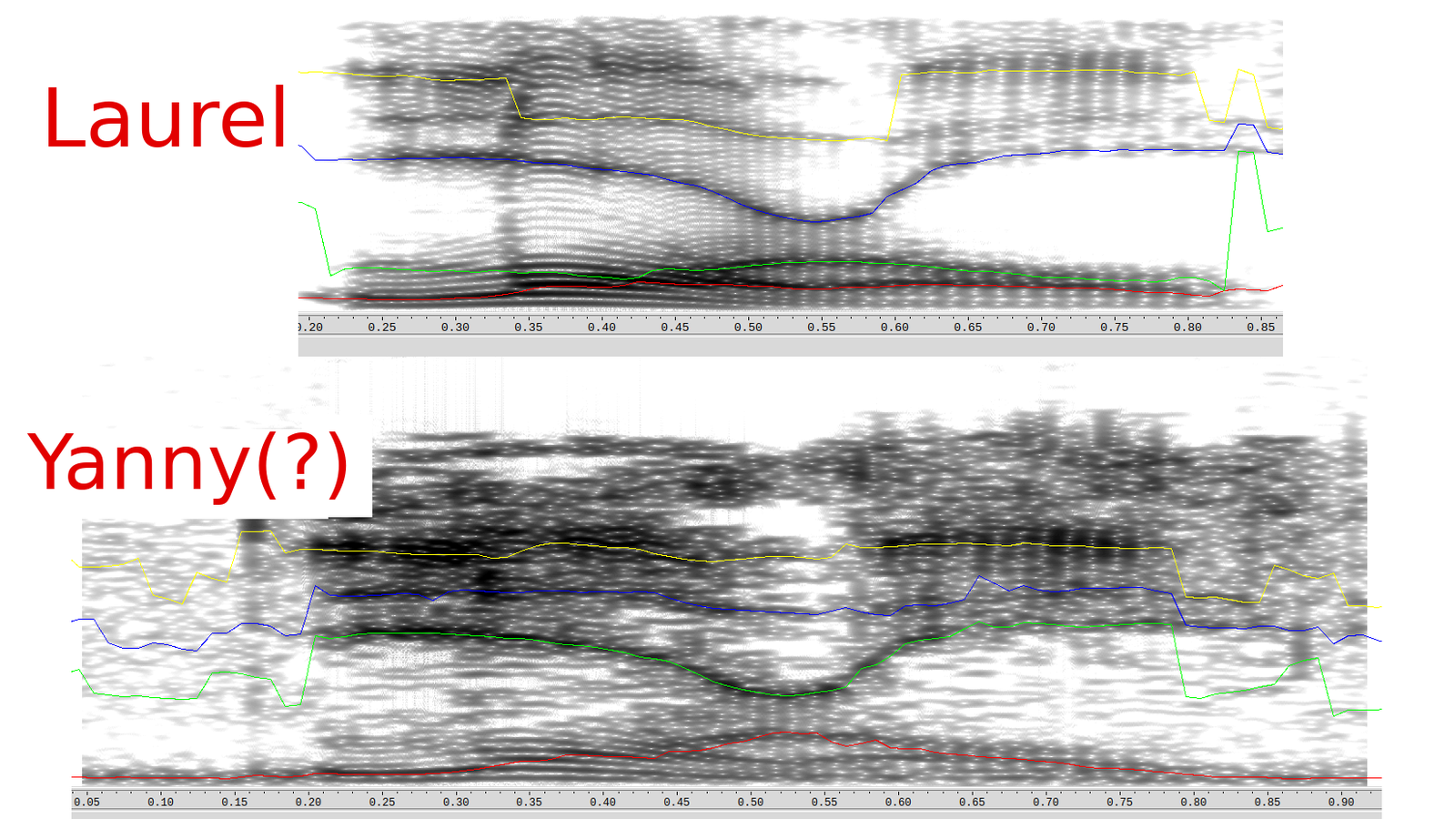
In the beginning, the laurel-or-yanny clip said laurel and nothing but laurel. Here is the original version of the clip, recorded by an opera singer working for Vocabulary.com. Chances are, you’ll hear it as laurel too. Let’s compare it to the viral clip and we’ll see exactly what changed, and why half of us hear the viral clip as yanny.
The original recording came from Vocabulary.com’s 2007 effort to include pronunciations for the site’s most commonly looked-up words. This was the recording made for the word laurel. It was spoken by Jay Aubrey Jones, one of eight singers commissioned by the company to read the words from home using a provided laptop, microphone, and portable sound booth. (Opera singers are trained to read IPA, the pronunciation code that dictionaries also use.) Jones personally read about 36,000 words for the site.
There were so many sound clips to process, says Vocabulary.com co-founder and chief technical officer Marc Tinkler, that software did everything automatically: trimming the beginning and end of each file, applying a noise-reduction filter if needed, and converting to the mp3 format that saves space and bandwidth.
The beauty of the mp3 format is that it can compress sound files into a small enough amount of space to easily share around the internet. The drawback of the mp3 format is that it does this by removing sounds from the recording and introducing some glitchy, tinny noises. If you’re okay with a file that’s only slightly compressed, you can leave in most of the original sound information. But, says Tinkler, “this was back in 2007 or 2008, so we were pretty aggressive in the downsampling process.”
I asked Tinkler if there was any chance he had the original file for comparison. He found it on a DVD in a storage closet, and uploaded it to Soundcloud for all to hear. Technically this is not the exact original, because Soundcloud provides it as an mp3 but it was originally recorded in an even higher quality format. But it’s more original, shall we say, than the version you and your friends have been arguing over. And it’s clear enough that we can now tell exactly what happened when the file was compressed.
What Got Lost
Compressing the laurel clip had a major casualty: the second speech formant. Without this part of the sound spectrum, an L can sound like “ee” and an R can sound maybe a little bit like an N.
Here’s why. Sound waves each have a frequency. The higher the frequency, the higher the pitch we hear. But the sound of speech includes many frequencies at the same time. Our ears and brains pick out the strongest frequencies from this mess of sound. Speech scientists call these formants. The two lowest-pitch formants give us enough information to tell the difference between one vowel sound and another.
If you open up a sound file in an analysis program, you can see these formants. That’s exactly what my father, a speech scientist at California University of Pennsylvania, did when I showed him the viral clip. He opened the mp3 in a program called Wavesurfer and proceeded to show me, on his laptop at the kitchen table, how I was wrong to hear laurel because the formants match up to the sounds “ee”, “a”, something ambiguous that could be an “n”, and a final “ee.” Yanny.
But, he conceded, there’s just enough ambiguity that you could hear laurel if you really wanted to. (He suspected at first that the file was carefully crafted to be ambiguous, an intentional audio illusion.) For the record, I have never heard anything but laurel from this file.
My dad can read the formants just from the black-and-white spectrogram view, but Wavesurfer helpfully detects them and color-codes them. Wavesurfer agrees with my dad, and reads this file as saying yanny. But if you give it the original file, it highlights a different set of formants: the ones that say, very clearly, laurel.
To understand what happened, take a look at the red and green lines. These are the first two formants, which we’ll call F1 (red) and F2 (green). They both hover around the bottom of the spectrogram. A third formant, F3, floats high above them in blue, dipping down very close to the F2 during the R sound in laurel.
But then look at the processed clip, the one that you’ve been sharing with your friends. (Click the arrow in the slideshow above.) It’s noisier overall, thanks to the mp3 compression. That noise blurs out the difference between the F1 and F2, leaving both Wavesurfer and our brains to figure there’s maybe only one formant down there, the F1. That means that the higher-up line, the one that dips down in the middle, looks like it must be the F2.
At the beginning of the clip, the F1 and F2 down low next to each other are compatible with hearing an L. But if F1 is down there, and F2 is way up above 2000 hertz, that’s an “ee” or a Y sound. Obliterating the second formant changes how we interpret the sound.
But There’s Enough Room to Disagree
The viral, processed clip doesn’t entirely remove the second formant, just makes it harder to discern among the noise. If you’re expecting to hear laurel, and if your ears and brain can find two formants in the low frequencies, you can still hear it as laurel. But to a different person, the sounds of yanny might stand out more, as Gizmodo reported earlier this week.
So what about those videos and slider tools that show you can change what you hear by listening to just the high or the low frequencies? It turns out that phenomenon, too, comes down to the speech formants.
If you cut off the higher frequencies, you’ll be left with just the lower part of the spectrum, where the original F1 and F2 were. Your brain will work a little harder to be able to tell those two formants apart, instead of locking on to what it thinks is an F2 higher up. By contrast, if you listen to just the higher frequencies of the clip, your brain picks up on the real F3 as a possible F2, and assumes there must be a single F1 down in the lower part of the spectrum.
So this trick changes your perception not because yanny is “in” one part of the spectrum and laurel “in” another, but because either way your brain is only hearing some of the formants, and is guessing at what the others might be.
Tech
via Lifehacker http://lifehacker.com
May 18, 2018 at 10:38AM
